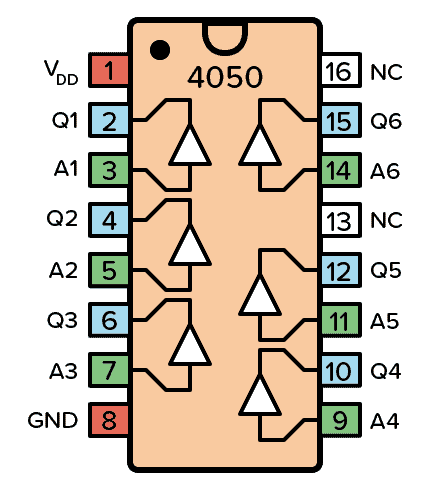
The CD4050 is a hex non-inverting buffer gate with 16 pins. It contains 6 buffers and is capable of driving two TTL/RTL loads or four 74LS loads. It can be used for buffering or level-shifting signals from a higher to a lower voltage.
Pin Overview
| Pin Name | Pin # | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | 1 | Power | Supply Voltage (+3 to +15V) |
| GND | 8 | Power | Ground (0V) |
| Q1-Q6 | 2, 4, 6, 10, 12, 15 | Output | Outputs from the buffers |
| A1-A6 | 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 14 | Input | Inputs to the buffers |
| NC | 13, 16 | – | Not Connected |
What is a Buffer/Converter?
A buffer is a device that takes an input and gives out the same. This might sound useless at first but is actually very useful for devices that have very low current output.
For example, the CD40106 can only sink 2.6 mA from each of its outputs. But if you connect a buffer from the CD4050B chip to the output, suddenly you can sink up to 48 mA, almost 20 times as much!
How to Use the CD4050 in a Circuit?
To use the CD4050 in a circuit, you need a power supply voltage of 3 to 15V (some versions support up to 20V, so check the datasheet of your version). Connect the power supply voltage to the VDD and GND pins of the chip.
Then, connect the logic signals you want to convert to the input pins of the buffers. And the output pins from the buffers to whatever you want to control. You can use as few or as many buffers as you want.

Note that it’s a good practice to connect any unused inputs to VDD or ground. Otherwise, you might risk that noise on the inputs makes the buffers switch on and off rapidly and cause the chip to consume more power than needed.
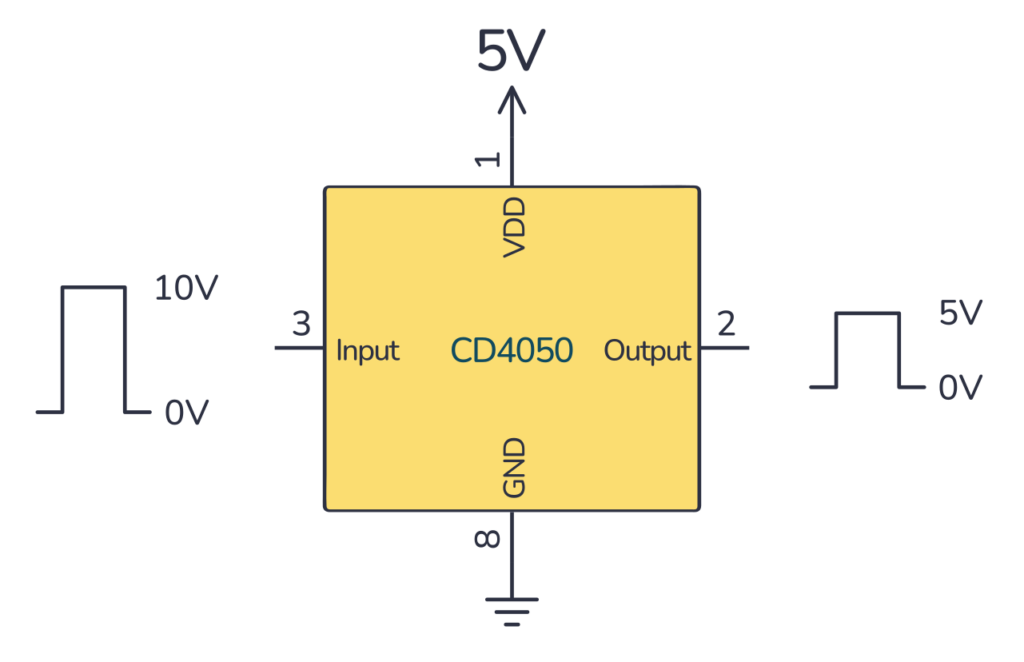
CD4050 Example Circuit – 5V Level Shifter
A common circuit example of the CD4050 is a level shifter that shifts down to 5V logic from for example 10V logic so that you can use it to control a 5V microcontroller, such as an Arduino. To make this circuit, you’ll need a 4050 IC:
Alternatives and Equivalents for CD4050
The 4050 IC always has a prefix and/or a suffix, such as CD4050BE, NTE4050, HEF4050, TC4050BP, MC14050, or HCF4050. This is to identify the manufacturer of the chip. But the functionality and the pins remain the same.
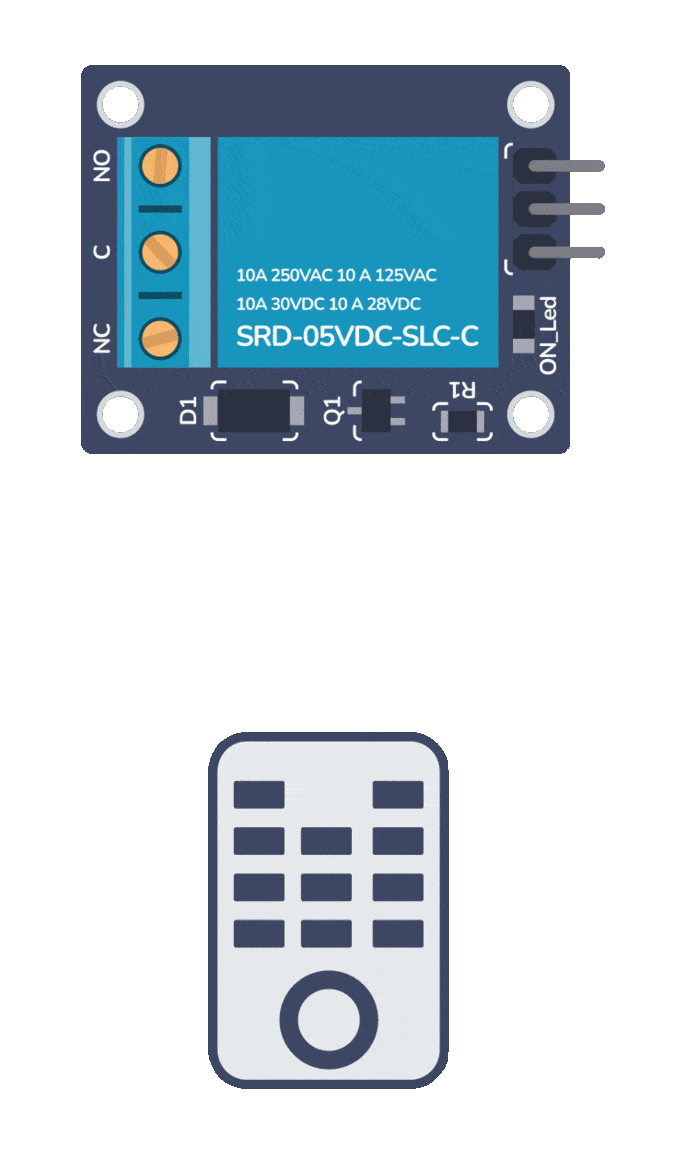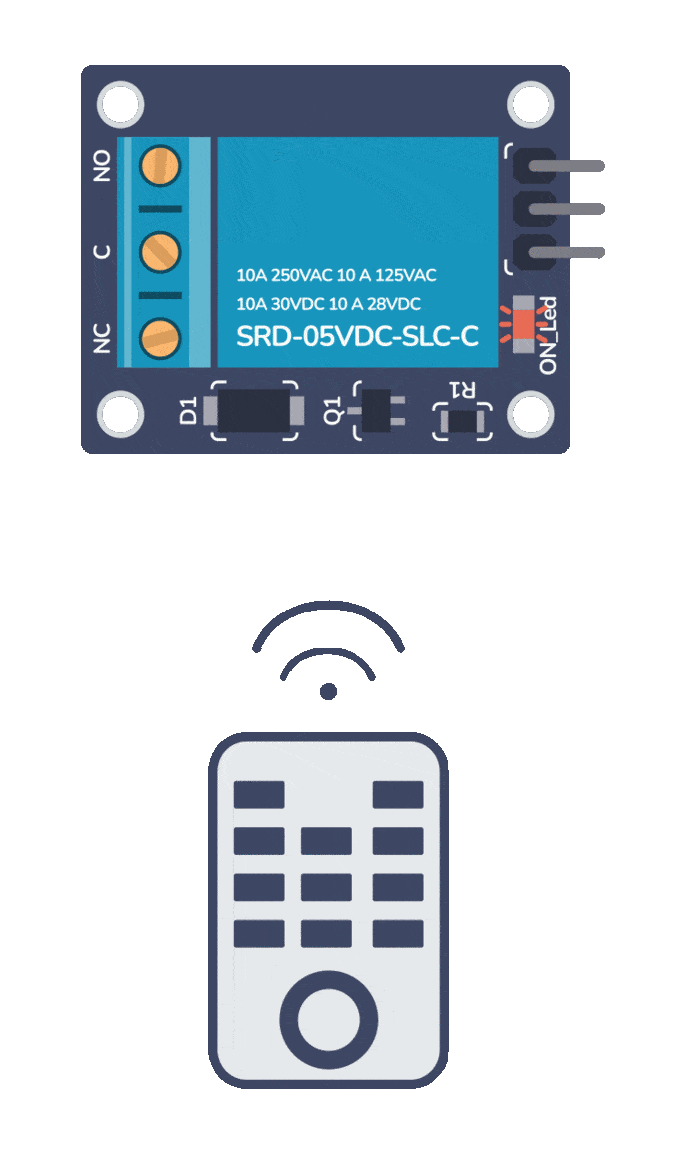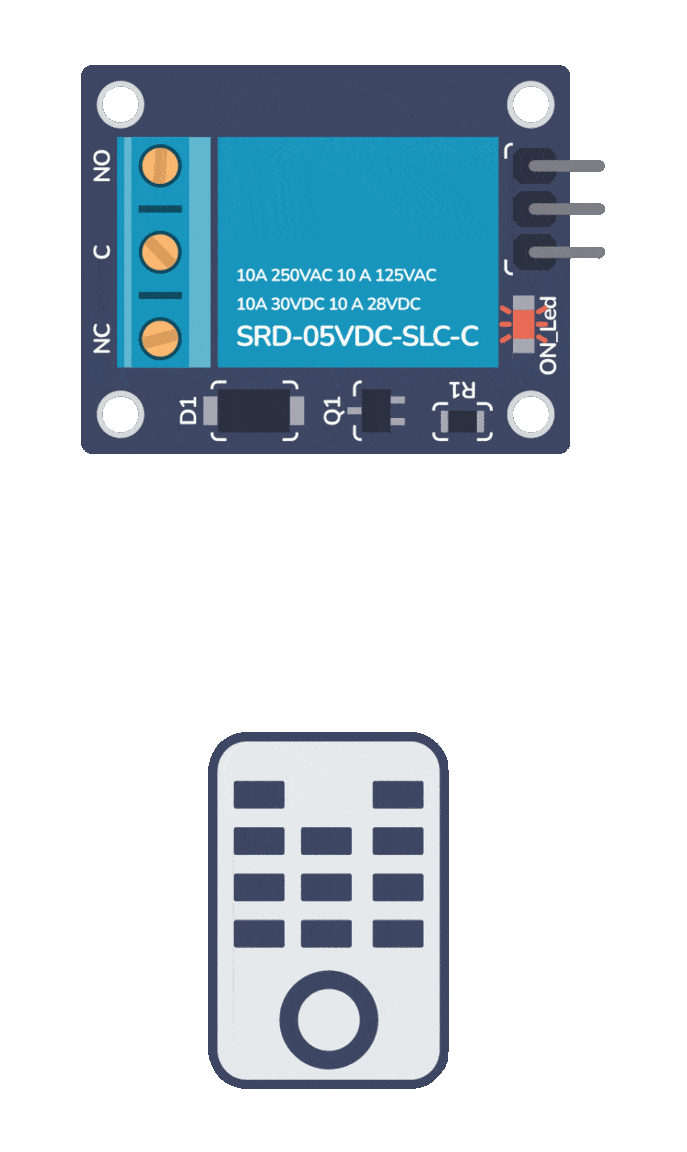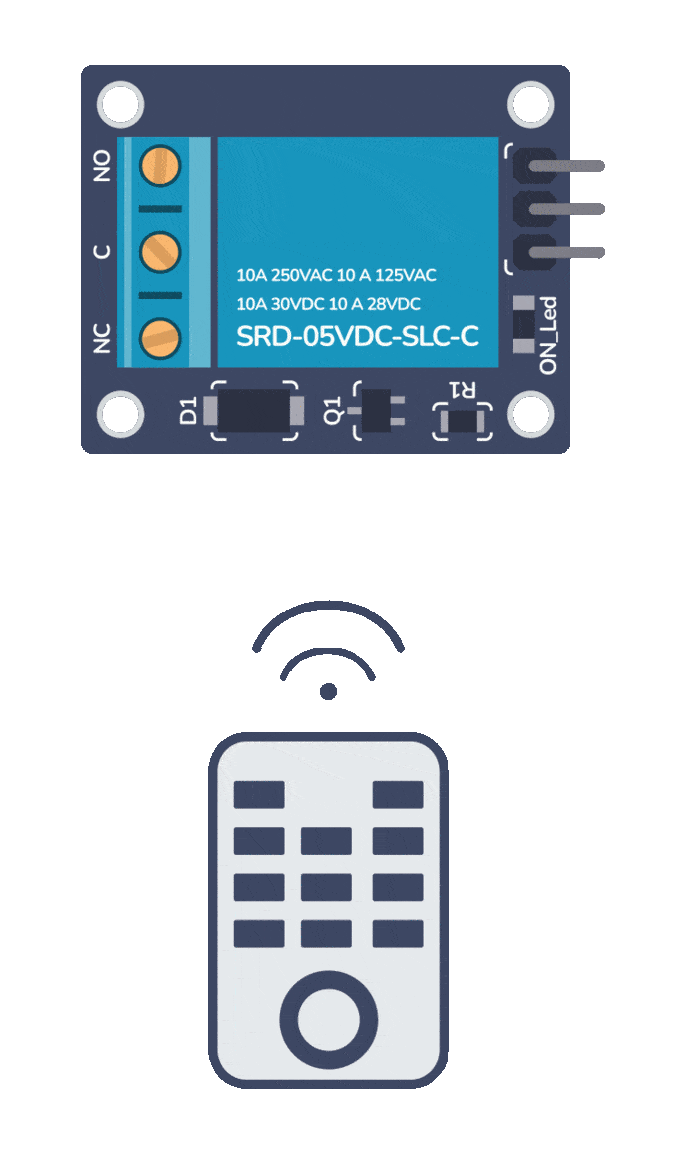
Build Something Useful This Evening
This gadget lets you use any IR remote-control to control your lamp, garden lights, heater oven, garage door, or anything else.
If you can’t find any of these chips in your local electronics store, check out my list of online stores where you can find components and tools for all your electronics projects.
Can’t find the 4050 anywhere? Then try one of the following IC alternatives:
- 4049: Inverting version of the 4050
- 74HC07: Hex Buffer Gate (not pin-compatible)
4050 Datasheet
Download the PDF datasheet for the IC 4050 here:
Go back to the full overview of the 4000-series integrated circuits
Get the 555 Timer Cheatsheet
A super helpful reference that makes it easy to design circuits, so that you can build oscillators, timer circuits, and more in no time.