The 74×05 (also known as 74HC05) is a chip with six open-collector inverters – or NOT-gates. An open collector output means you can hook it up to different logic levels easily. But, it also means the outputs behave a little bit differently from a standard NOT gate chip.
In this guide, you’ll learn what this chip does and how you can use NOT gates for whatever it is you’re making.
What does the 74HC05 / 74LS05 do?
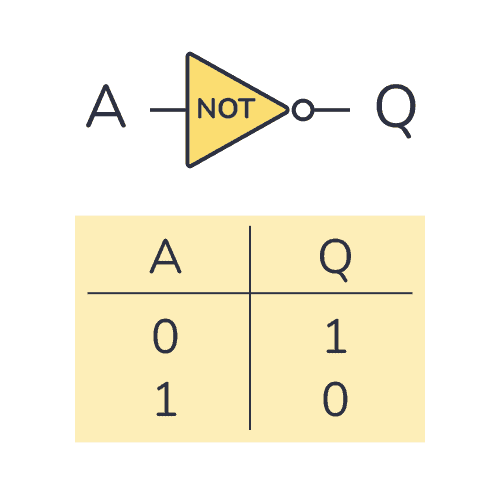
The 74×05 gives you six NOT gates. Each with an open-collector output. A NOT gate (or inverter) is a logic gate that outputs the opposite of the input. In the truth table below, you can see what the output will be for any given input:
How To Use This Chip
The 74HC05 comes in a 14-pin package.
First, you need to connect it to power. Then you can use any of the gates inside it. Most 7400 ICs support a VCC voltage of 5V. One difference to make note of between the HC and LS versions is that 74HC05 supports 2V to 6V, while the 74LS05 only supports 5V.
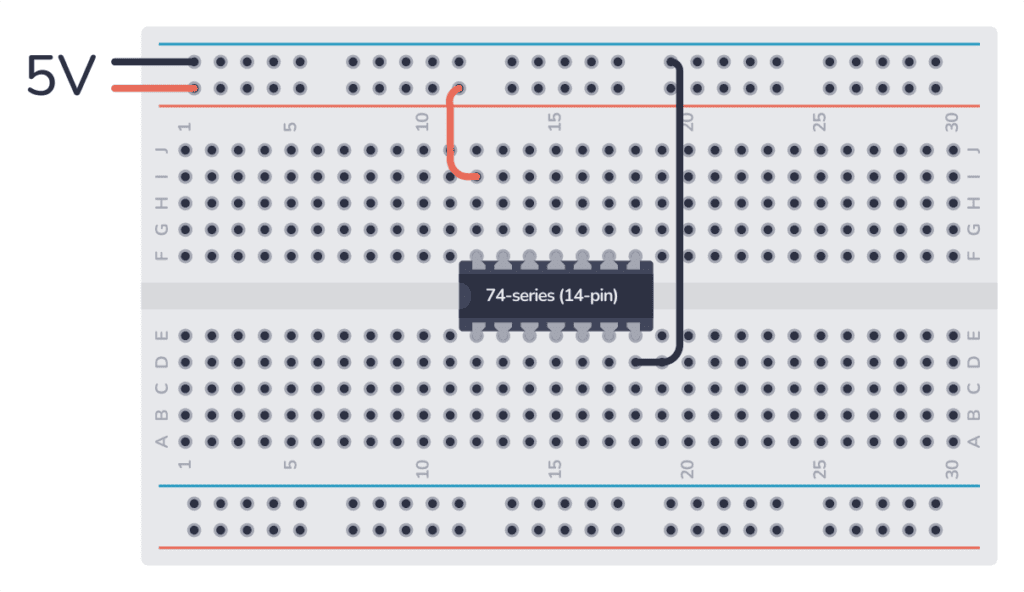
Once you’ve connected the power, you can use any of the six open-collector inverters inside.
Keep in mind that this chip has open-collector outputs which means you can only sink current, not source it.
The output of each gate in the 74HC03 can sink around 4 milliamps when it’s powered with 5 volts. On the other hand, the 74LS03 can usually handle about 8 milliamps of current. But, these values might differ depending on the chip manufacturer.
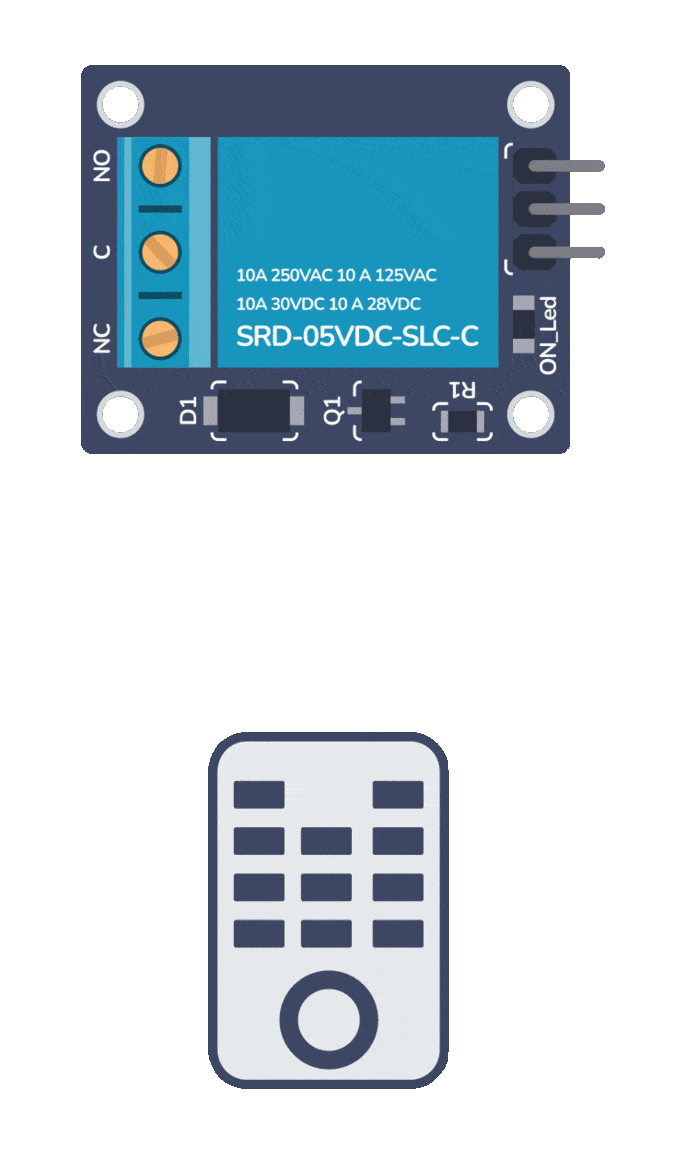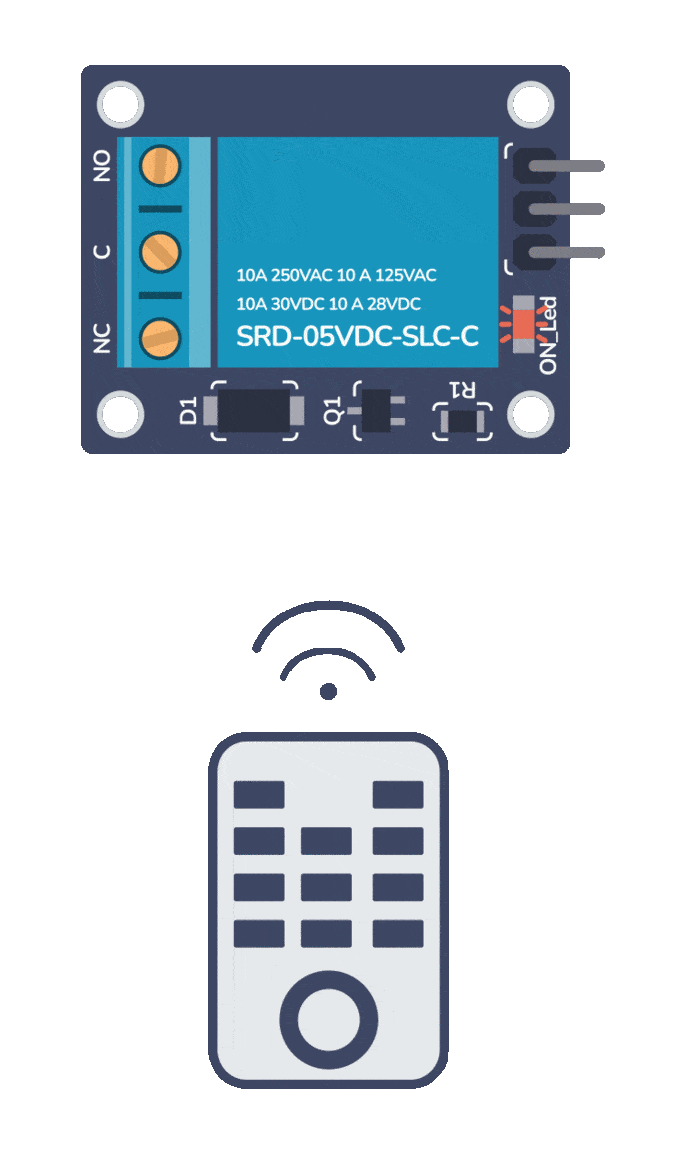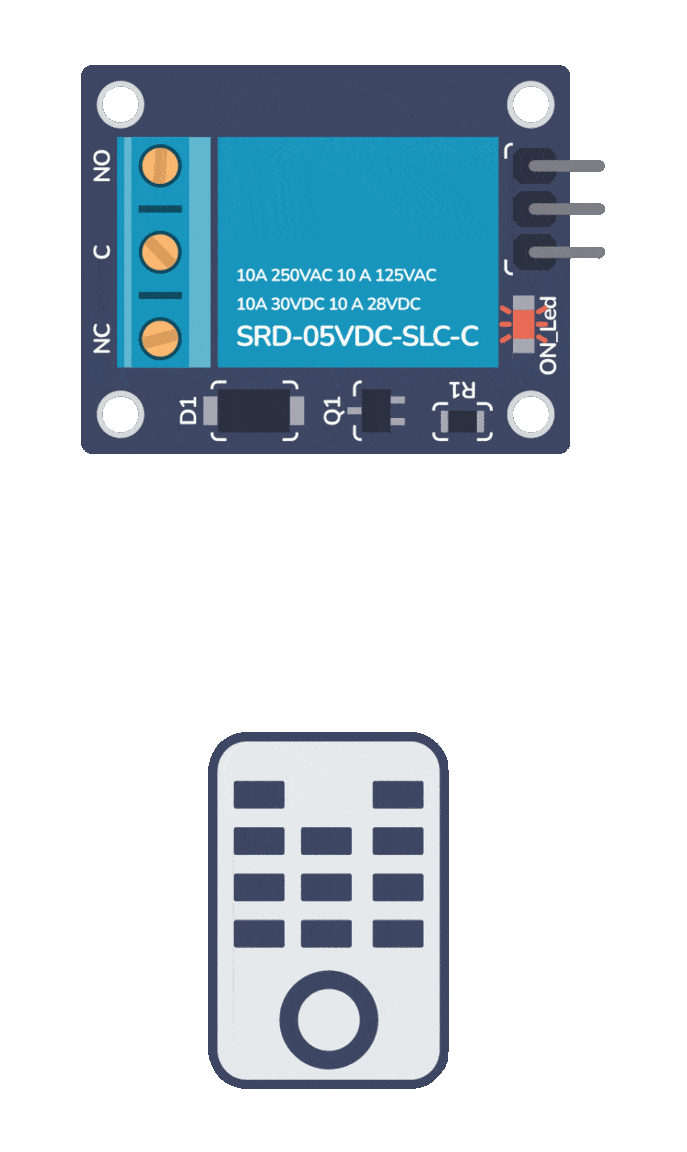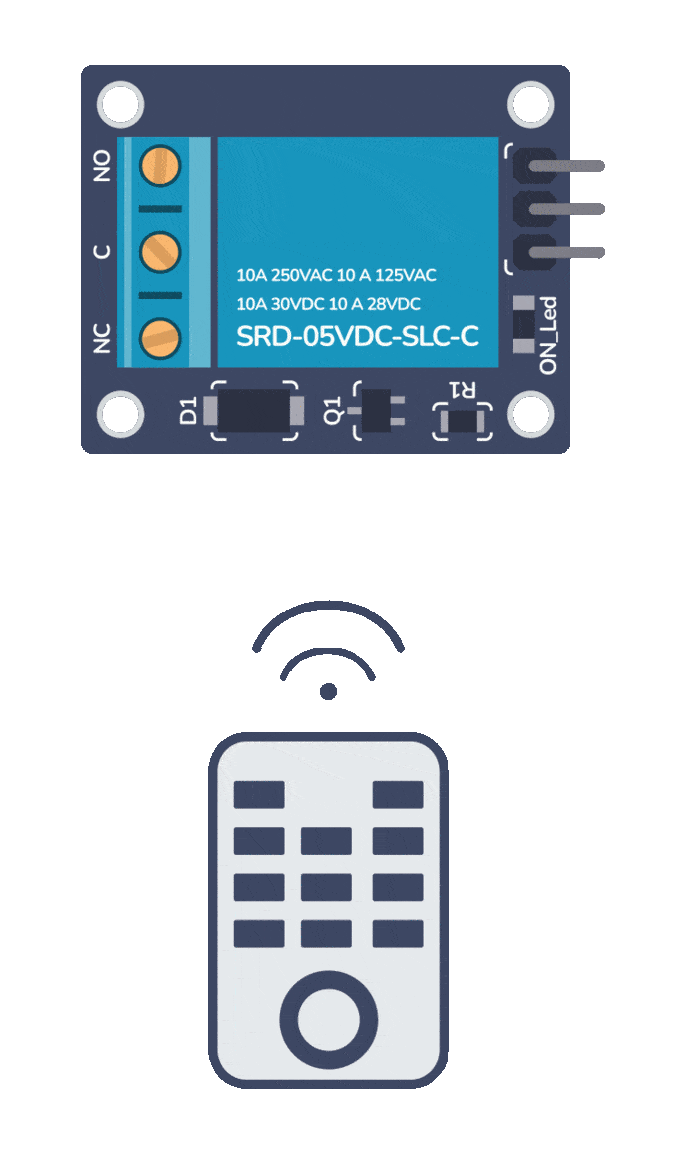
Build Something Useful This Evening
This gadget lets you use any IR remote-control to control your lamp, garden lights, heater oven, garage door, or anything else.
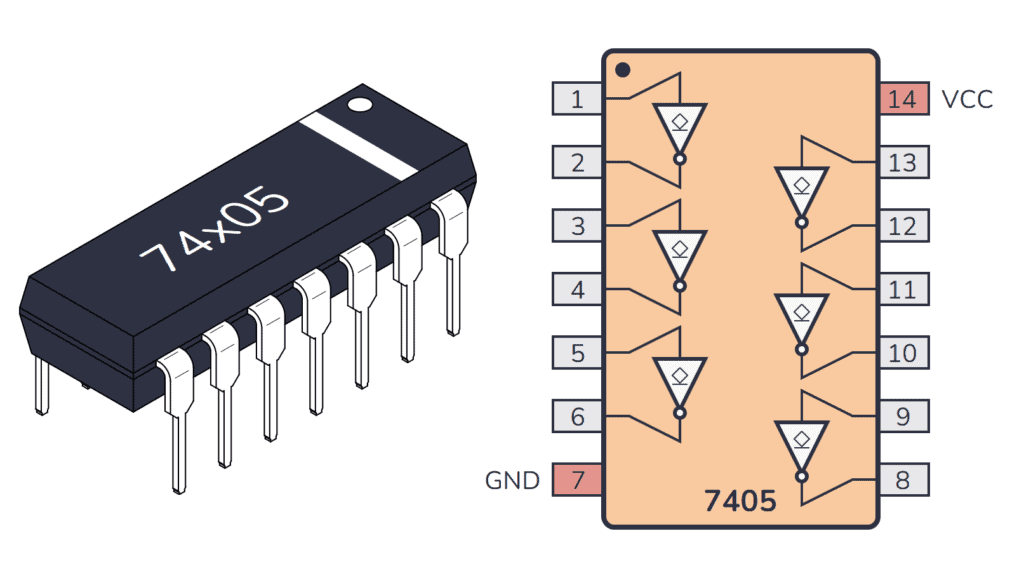
74×05 Pinout
The 74×05 has 14 pins and has six inverters laid out as shown in the pinout diagram below:
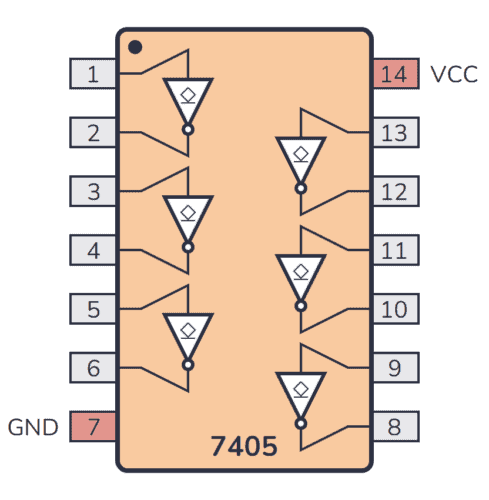
| Pin # | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input | Input to the first NOT gate. |
| 2 | Output | Open-collector output from the first NOT gate. |
| 3 | Input | Input to the second NOT gate. |
| 4 | Output | Open-collector output from the second NOT gate. |
| 5 | Input | Input to the third NOT gate. |
| 6 | Output | Open-collector output from the third NOT gate. |
| 7 | Power | Connect to ground (GND). |
| 8 | Output | Open-collector output from the fourth NOT gate. |
| 9 | Input | Input to the fourth NOT gate. |
| 10 | Output | Open-collector output from the fifth NOT gate. |
| 11 | Input | Input to the fifth NOT gate. |
| 12 | Output | Open-collector output from the sixth NOT gate. |
| 13 | Input | Input to the sixth NOT gate. |
| 14 | Power | Positive power supply (VCC). Connect to +5V power. |
Alternatives and Equivalents for 74HC05 / 74LS05
There are many versions of the 74×05 chip. They all have the same functionality but with different specifications such as supported voltages and maximum current output.
Here’s a list of a few equivalents of this chip:
- 74HC05 (High-speed CMOS)
- 74HCT05 (High-speed CMOS, TTL compatible)
- 74LS05 (High-speed TTL)
- 74LVC05 (Low Voltage TTL)
- 74AC05 (Advanced CMOS)
- 74ALS05 (Advanced Low-Power Schottky TTL)
- 74F05 (Very High Speed)
- 74C05 (CMOS, similar to the 4000-series)
Some manufacturers also add a prefix, such as the SN74HC05 and SN74LS05 by Texas Instruments.
Can’t find the 74×05 anywhere? Then try one of the following IC alternatives:
- 74×04 – Hex inverters.
- 74×14 – Hex inverters (with Schmitt-trigger inputs).
- CD4049 – Hex inverting buffers/converter.
- CD4069 – Hex inverters/NOT-gates.
- CD40106 – Hex inverters (with Schmitt-trigger inputs).
If you can’t find the 74×05 IC in your local electronics store, don’t worry, you’ll most likely find it in one of the stores listed on this page of online stores where you’ll find components and tools for all your electronics projects.
Datasheet for the 74LS05 and 74HC05 chips

10 Simple Steps to Learn Electronics
Electronics is easy when you know what to focus on and what to ignore. Learn what "the basics" really is and how to learn it fast.